
- (619) 483-4180
- info@avantiico.com
Product Selection Tools
Evaluation Guides
Readiness Overview
Identifying Stakeholders
Managing Expectations
Prepare to be Prepared
Upgrade Services
Project Management
Roadmap Services
Data Migration
Data & Analytics
Avantiico Industry Solutions
Explore by Business Need
Avantiico Industry Solutions
Microsoft Platforms
Licensing & Pricing Options
Our Partners
Careers
Avantiico Academy Program
About Avantiico
Events & Webinars
Core Services
Core Solution Areas
Recent Blog Posts
Featured Blog Posts
Common Data Model (CDM) is a standard for defining data structures and relationships between them. The declarative language of CDM allows independently developed applications to have a common data management and storage engine. Initially developed for integration across the Microsoft product lineup, it is now open source and grows on a regular basis. Businesses can now benefit from the ideas shared by the community members specific to their sector or industry at no cost. Data stored in CDM is not affected by the way was created and becomes portable between the apps, making it available for processing and analyzing at every possible angle.

Developed by Microsoft in close collaboration with its business clients from automotive, banking, commerce, educational, healthcare, marketing, sales, legal and non-profit institutions over decades of data management as a collection of standard data definitions (called entities) Common Data Model seamlessly integrates all Microsoft product lineup, including Office 365, Dynamics 365 and Azure.
The extensive collection of the standard entities are further enhanced with the relevant metadata on relationships, attributes and semantics.
Standard entities of the Common Data Model describe commonly used objects and activities across almost every business: Account, Contact, Product, Service, to name a few out of more than 333. The number of available entities has been growing at a tremendously high speed after Microsoft changed CDM to be an open source community.
Historically, the way of handling the data has been influenced by the function of a specific app. Accounting app would store and process the data similar to a Commerce app in a different way, more convenient from the accounting standpoint. Enabling these two to exchange the data does not require building custom solution, if a CDM is used.
Now anyone can create and extend custom entities without the risk of disrupting the existing data links. Businesses take advantage of the ideas shared by the community members specifically for their area at no cost.


Importing data into CDM requires mapping to the standard entities, or creating custom ones. Abundance of publicly available mapping templates makes importing fast and easy. Data stored in Common Data Model remains secure, as each business maintains full control over what exactly is shared with the other apps.
With Common Data Model, any process or application can get a permission to analyze, process and unlock every bit of meaningful information from the data shared with it. For marketing this means new trends and insights, for sales and services – more personal customer engagements, and many more. Developers use CDM for simplified data access and management, rapid app building and deployment. Even computers themselves are using it for Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.
Horizontal data integration provided by CDM is further extended by free industry accelerators from Microsoft – collections of foundational components for rapid deployment of industry-specific vertical solutions. Currently Microsoft has developed the accelerators for Automotive, Banking, Insurance, Educational, Healthcare, Non-profit, Manufacturing, Media and Entertainment industries with many more to come.
Microsoft Dataverse relies on CDM for secure data storage and across the entire Office 365, Dynamics 365 and Power Platform product lineup, extending functionality and analysis capabilities as well as speeding up workflows, solutions and app development.
The data inside CDM is stored in folders, one for each entity. The folder has a metadata file called manifest which holds detailed entity description in a human-readable JSON format and a number of data files in a comma-separated value (CSV) format. All entities within the model, their relationships and interactions are encapsulated in a master object named corpus. It also includes an object library that creates and manages the Common Data Model folder metadata files, allowing for data type customization at any level. It also holds the version information for the entity. Both the manifest and schema definition files allow for import of other definition documents.


Industry accelerators include powerful connected experiences that are designed to support common, existing business needs for specific industries, enabling solutions that deliver new insights and more personalized customer engagements. This helps simplify efforts to procure partner solutions or build custom applications by providing access to a unified data layer that saves customers the time and resources they would have spent creating their own proprietary data layer or attempting to integrate disparate systems and solutions
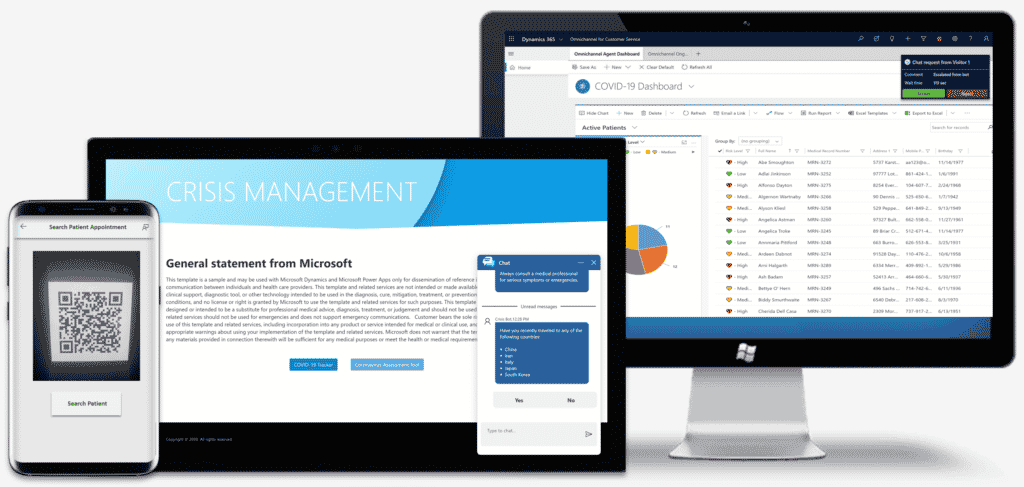
Currently available industries are: automotive, healthcare, nonprofit, education, manufacturing and supply chain, media and communications, banking and finance with the others being added on a regular basis. Each accelerator is being developed by an open community managed by Microsoft, where specific businesses share and implement their best practices and ideas.
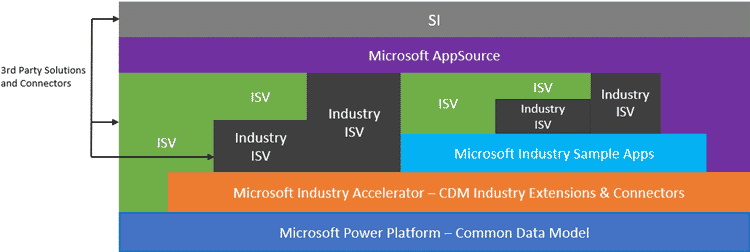
Since Dataverse is built around a Common Data Model, industry accelerators are providing exciting opportunities to the independent software vendors (ISVs) to build on top of any level of the platform and accelerators:
600 B Street, Suite 300, San Diego, CA 92101 | (619) 483-4180 | info@avantiico.com
Discover how Avantiico helps you improve business processes, provide customers with a seamless experience and transform the way you do business.
Discover how Avantiico helps you improve business processes, provide customers with a seamless experience and transform the way you do business.